Introduction to Memory Consolidation
Memory grows stronger during sleep because the brain organizes new information into structured patterns. The mind collects facts, experiences, and emotions through the day and sorts them during rest. This organization increases stability and improves recall because strong connections help the brain access details faster. Sleep removes unnecessary information and sharpens important knowledge, which helps students understand lessons better. The brain builds memory efficiently when it receives consistent rest because it needs uninterrupted time to strengthen connections. Students who protect their sleep gain real advantages in focus and retention.
Why the Brain Needs Sleep for Learning
The brain cannot store information efficiently during constant wakefulness because distractions interrupt processing. Sleep gives the mind a quiet environment that supports deeper organization. Good rest improves memory accuracy because the brain strengthens new pathways during the night. Students learn faster and think more clearly when they sleep well because the brain maintains energy and structure. Sleep also supports motivation because fatigue lowers interest in learning. Consistent rest gives students stronger attention during class and helps them complete tasks with fewer mistakes.
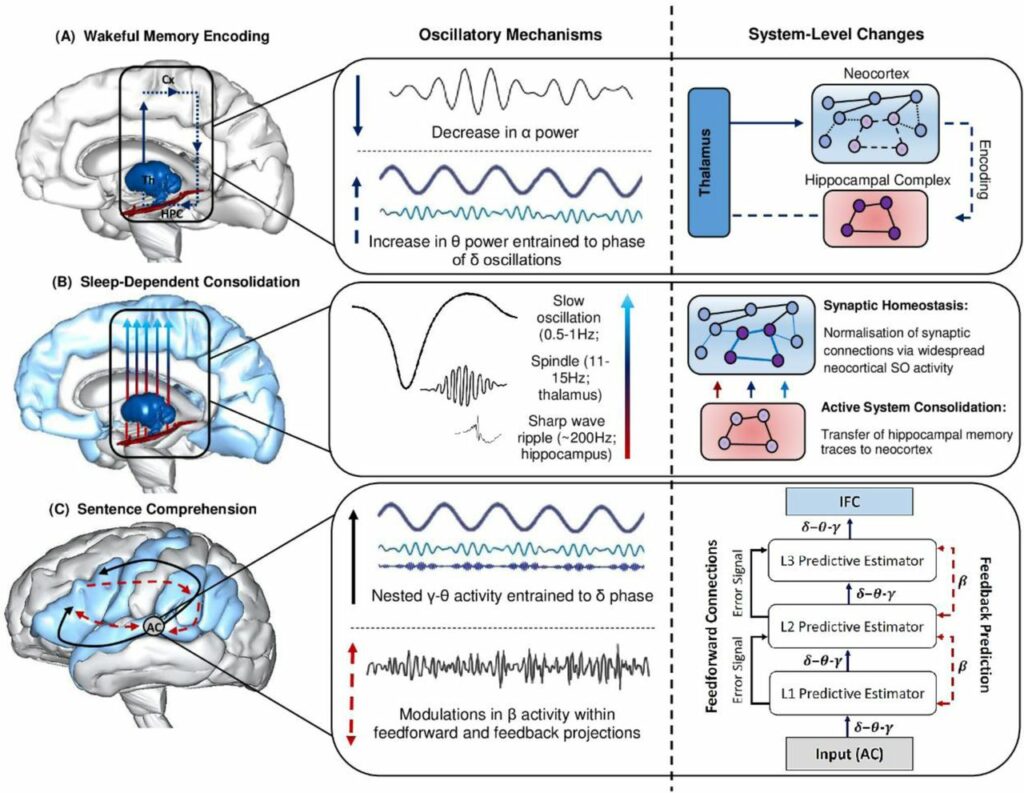
How Memory Forms After Learning
Memory begins the moment the brain absorbs new information because neurons respond to stimulation. These neurons build weak connections at first because the mind works quickly during active learning. Sleep strengthens these connections and turns them into stable memory networks. The brain reviews important information and forms categories that help with future recall. Students remember lessons better when the brain organizes concepts instead of leaving them scattered. This process protects long-term learning because organized knowledge stays accessible for years.
The Stages of Sleep
Sleep includes several stages that support memory in different ways because the brain changes rhythm throughout the night. Non-REM sleep begins the cycle and slows brain activity into a steady pattern. REM sleep follows and increases activity to handle emotional and creative processing. Deep sleep occurs inside the Non-REM phases and gives the brain time to strengthen physical and cognitive skills. These stages work together to support every type of memory because no single stage can handle all learning needs. Students gain strong results when they maintain full sleep cycles.
Non-REM Sleep and Basic Knowledge
Non-REM sleep builds foundational memory because it stabilizes facts and repeated information. The brain uses this phase to reinforce vocabulary definitions, math formulas, historical dates, and simple rules. Students perform better in basic subjects when they protect Non-REM sleep because this stage organizes and strengthens essential knowledge. The mind cleans up mental clutter during this phase and creates smoother pathways for recall. Strong Non-REM sleep leads to clearer thinking during tests and homework.
Deep Sleep and Skill Development
Deep sleep supports motor memory because the brain practices physical skills during this phase. Students who train in sports, music, experiments, or hands-on tasks gain sharper coordination when they sleep well. The mind improves balance, rhythm, and precision by replaying movement patterns learned during the day. Deep sleep increases skill accuracy because the brain adjusts weaknesses and strengthens strong patterns. Students who need athletic or technical performance gain major benefits from deep sleep.
REM Sleep and Emotional Memory
REM sleep processes emotional experiences because the brain uses high activity to study events with strong meaning. Students deal with stress, excitement, and pressure throughout the day, and REM sleep helps the brain reflect on those experiences. This reflection improves emotional understanding because the mind studies signals and patterns. REM sleep also supports creativity because the brain tests new combinations of ideas. Students who rely on complex thinking gain better performance when they maintain strong REM cycles.
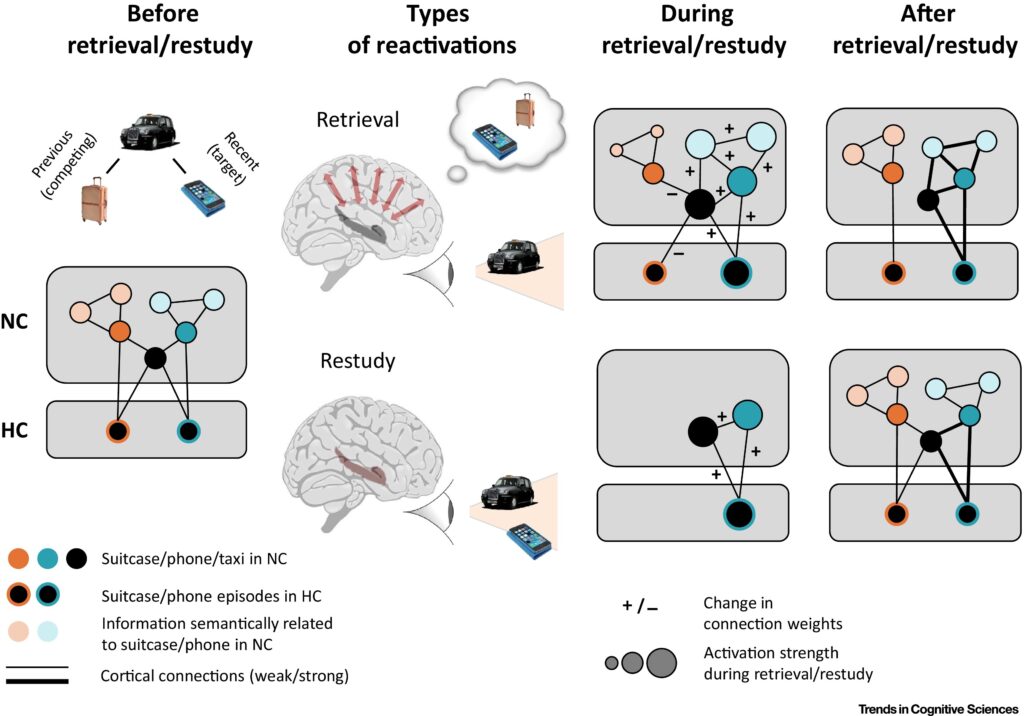
Neural Replay and Memory Strengthening
Neural replay strengthens memory by repeating important information at high speed. The brain compresses a full day of learning into fast bursts that reinforce critical pathways. Replay increases memory strength because repeated firing makes connections durable. Students recall facts faster when neural replay functions well because the brain builds efficient routes for retrieval. Sleep allows uninterrupted replay, which means the brain works intensely without distractions. Strong replay develops long-term memory that supports future learning.
The Role of the Hippocampus
The hippocampus handles new memory because it gathers information throughout the day. This region helps the brain store facts, experiences, and skills in temporary form. During sleep, the hippocampus shapes these memories into patterns and prepares them for long-term storage. Students need a strong hippocampus because it supports learning in every subject. Sleep protects the hippocampus and helps it perform its duties without interruption. A healthy hippocampus produces stable memories that last.
How the Cortex Stores Long-Term Memories
The cortex receives information from the hippocampus and builds long-term structures that support lifelong recall. The brain organizes details into categories because structure improves memory access. The cortex links new information with older knowledge to strengthen understanding. Students understand lessons better when the cortex organizes information effectively. Sleep gives the cortex enough time to arrange details into meaningful networks that help with comprehension and retrieval.
Sleep and Problem-Solving Skills
Sleep improves problem-solving because the brain creates connections between complex ideas during rest. Students understand difficult concepts better after sleeping because the mind organizes related information. Rest allows the brain to explore different approaches to problems and experiment with new solutions. Creative thinking increases during REM sleep because the mind tests unusual combinations of ideas. Strong problem-solving helps students with math, science, writing, and projects.
Sleep and Focus
Focus improves with sleep because the brain restores energy during rest. Students concentrate better after strong sleep because the mind stays sharp and clear. Tired brains struggle with attention because exhaustion blocks access to stored information. Sleep protects attention span and helps students absorb lessons without confusion. Good rest reduces mental fog and keeps thinking efficient for studying and completing tasks.
The Effect of Poor Sleep on Learning
Poor sleep weakens memory because the brain cannot complete its nightly consolidation cycle. Students forget important details when rest drops because unstable connections fade quickly. Tired minds struggle with reasoning because the brain loses clarity during exhaustion. Poor sleep increases stress and reduces motivation, which harms academic performance. Students who skip sleep experience slower recall, weaker comprehension, and more difficulty during tests. Consistent poor sleep also harms long-term learning because the brain fails to store information properly.
Sleep and Academic Performance
Students who maintain strong sleep habits earn better grades because their memory stays strong. Rest improves organization, comprehension, and performance in every subject. Sleep supports motivation and helps students complete assignments with fewer mistakes. Schools that promote sleep habits see improvement in test scores and class engagement because rested students think more clearly. Good sleep strengthens the connection between learning and recall, which improves overall success.
How Students Can Improve Sleep
Students can improve memory by developing strong sleep routines because rhythm helps the brain prepare for rest. Going to bed at the same time each night creates predictable cycles that strengthen memory. Turning off screens before sleep reduces stimulation and helps the mind relax. Students gain better sleep when they avoid caffeine before bed and create a calm environment. Small adjustments lead to large improvements in learning because sleep supports every part of memory.
Why Teenagers Need Extra Sleep
Teenagers need more sleep because their brains grow rapidly during adolescence. Growth increases memory demands because new skills and knowledge develop at fast rates. Teen brains process emotional experiences more intensely, which increases the need for healthy REM cycles. Students who ignore their sleep needs struggle with mood balance, energy, and learning. Strong sleep supports stable emotions and sharp thinking.




Add comment